Initiating preparation for GATE Architecture exam is the first step toward building a great career. Your work isn’t started yet, though. We recommend you to go through the GATE Architecture & Planning syllabus once.
What if we provide a complete checklist that you can download and print and refer to every time while preparing?
It’s a great idea to begin your preparation with confidence, undoubtedly increasing your chances of success.
So, how can you tweak, and what are the steps involved to optimize your preparation?
First, let us familiarize you with the GATE Architecture syllabus, where all the magic happens, and then jump to your preparation.
GATE, also known as the Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering, is an exam held in India to evaluate knowledge in engineering, science & Technology at the Postgraduate level. The syllabus and importance of topics covered in GATE may have slight variations each year, so it is crucial to refer to the official GATE website or the organizing institute’s website for the latest information. However, Dkosh.com (Design-Kosh) can provide you with a general overview of the GATE Architecture Planning syllabus for your convenience.
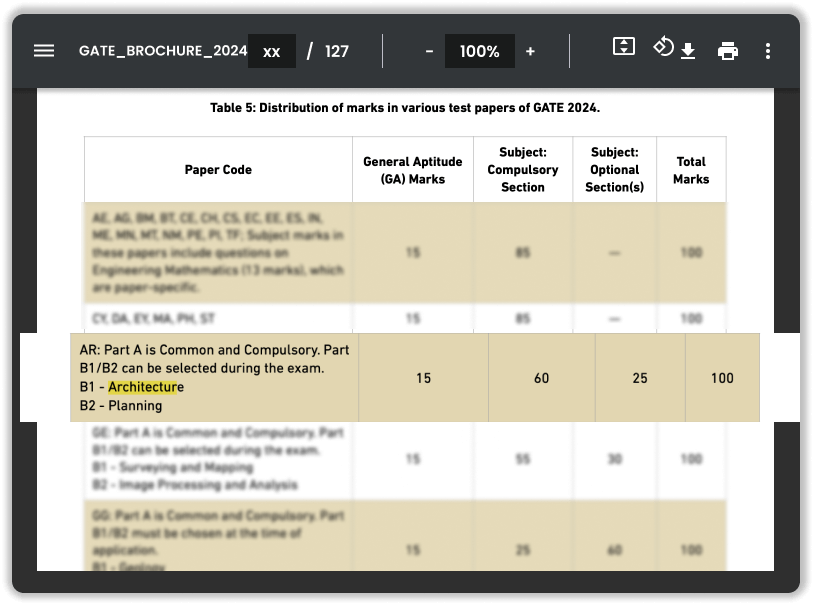
Source: https://gate2024.iisc.ac.in/download/
Part A: Common for (GATE Architecture syllabus)
Section 1: Architecture, Planning, and Design
This part of the GATE Architecture & Planning exam syllabus focuses on important subjects related to architectural graphics, planning, and design principles. Candidates will be assessed on their understanding of visual composition in both 2D and 3D, as well as the use of computer applications in architecture and planning. Additionally, anthropometrics, which involves studying human body measurements and proportions, will be covered.
Other topics in this section include the arrangement of space in both horizontal and vertical dimensions, as well as space standards. Candidates should also be familiar with universal design principles that aim to create accessible environments for all individuals. Knowledge of building bye-laws, codes, and standards is crucial for this section.
Section 2: Construction and Management
In this section, candidates will be examined on their understanding of construction techniques, methods, and management. They will need to demonstrate proficiency in project management techniques like PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method). Estimation and specification of construction projects are also important aspects of this section.
Additionally, candidates must understand professional practice, ethics, principles, and design of disaster-resistant structures. Candidates will be tested on their knowledge of temporary structures used for rehabilitation purposes. All ALL those topics will be covered in the examination.
Section 3: Environmental Planning and Design
This section focuses on environmental considerations in planning and design. Candidates will need to understand natural and man-made ecosystems and ecological principles. Environmental pollution and its types, causes, controls, and abatement strategies will be covered.
Sustainable development, climate change, and their implications on the built environment will also be part of this section. Candidates should be familiar with climate-responsive design principles that help create environmentally friendly structures.
Section 4: Urban Design, Landscape and Conservation
Urban design, landscape planning, and conservation are the key components of this section. Candidates will need to study historical and modern examples of urban design, along with elements of the urban built environment such as urban form, spaces, structure, pattern, fabric, and texture.
Principles, tools, and techniques of urban design will be assessed, along with the importance of public spaces, character, spatial qualities, and a sense of place. Urban design interventions for sustainable development and transportation will also be covered, including development controls like FAR (Floor Area Ratio), densities, and building byelaws.
Urban renewal, heritage conservation, historical public spaces, gardens, and landscape design will also be part of this section, along with site planning.
Section 5: Planning Process
This section focuses on various concepts, theories, and principles of urban planning. Candidates will need to understand the concepts of cities such as Eco-City and SmartCity, as well as ekistics (the science of human settlements).
Urban sociology and social, economic, and environmental cost-benefit analysis are also essential topics. Methods of non-spatial and spatial data analysis will be examined, along with development guidelines like URDPFI (Urban and Regional Development Plans Formulation and Implementation).
Section 6: Housing
Housing typologies, neighborhood concepts, and residential densities will be tested in this section. Candidates should be knowledgeable about affordable housing and real estate valuation.
Section 7: Services and Infrastructure
This section focuses on various services and infrastructure related to buildings. Topics include firefighting systems, building safety and security systems, water treatment, water supply and distribution systems, water harvesting systems, and stormwater drainage systems.
Candidates will also need to understand sewage disposal methods, solid waste management, recycling, and reuse of solid waste. The inter-relationships between land use, transportation, and urban form will also be covered, along with the design of roads, intersections, parking areas, and pedestrian planning.
Part B1: Architecture (GATE Architecture syllabus)
Section B1.1: History and Contemporary Architecture
This part of the syllabus deals with the principles of art and architecture. Candidates will need to study the world history of architecture, including various architectural styles from different periods. Examples of contemporary architecture and the influence of modern art and design on architecture will also be included.
Indian vernacular and traditional architecture, as well as works of renowned national and international architects, will be tested in this section.
Section B1.2: Building Construction and Structural Systems
In this section, candidates will need to demonstrate their understanding of building construction techniques, methods, and details. Topics include building systems, prefabrication of building elements, principles of modular coordination, and construction planning and equipment.
Knowledge of building materials, strength of materials, foundations, and design of structural elements with different materials will also be assessed. Elastic and limit state design, structural systems, and principles of pre-stressing are other important topics.
Section B1.3: Building Services and Sustainability
Candidates will be examined on their knowledge of sustainable building strategies, solar architecture, and comfort factors in built environments. This section also covers topics related to ventilation, air-conditioning systems, building performance evaluation, and intelligent buildings.
Water supply, sewerage and drainage systems, plumbing, electrification of buildings, and standards for elevators and escalators will be tested.
Part B2: Planning (GATE Architecture syllabus)
Section B2.1: Regional and Settlement Planning
This part of the syllabus focuses on regional and settlement planning concepts. Topics include regional delineation, settlement hierarchy, types and hierarchy of plans, and various schemes and programs of the central government.
Candidates will need to understand Transit-Oriented Development (TOD), SEZ (Special Economic Zone), SRZ (Special River Zone), and public perception and user behavior. Knowledge of national housing policies, programs, and schemes, as well as slums, squatters, and informal housing, will also be assessed.
Section B2.2: Planning Techniques and Management
In this section, candidates will be examined on their application of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing techniques in urban and regional planning. They will also need to demonstrate proficiency in various survey techniques such as physical, topographical, land use, and socio-economic surveys.
Urban economics, graphic presentation of spatial data, planning legislation and implementation, decision support systems, and land information systems are other important topics. Urban geography, infrastructure project management, demography, and equity in planning will be included.
Section B2.3: Infrastructure Planning
This section focuses on transportation planning and traffic engineering. Topics include road capacity, travel demand forecasting, traffic survey methods, traffic flow analysis, and traffic management in urban areas.
Candidates will also need to understand mass transportation planning, intelligent transportation systems, and the urban and rural infrastructure system network.
Note: The above information is for informative purposes only. GATE Architecture Syllabus is controlled by GATE. Kindly visit the Official GATE website to get an updated GATE Architecture & Planning syllabus.
for B.Arch entrance visit NATA Architecture blogpost

